Chronic complication of diabetes | Type 1 | Examined | Initial stage | Macular edema | Proliferative stage | Development | Vitreous hemorrhage | Retinal detachment | Laser coagulation | Treating retinopathy | Control of diabetes | Glucose values | The presence of retinopathy | Avoid lifting heavy objects
____________
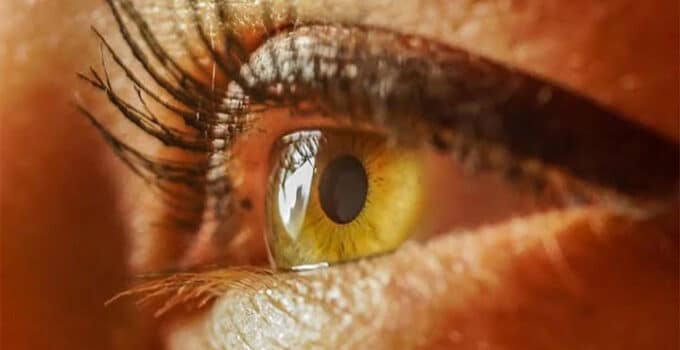
1. Chronic complication of diabetes
Diabetic retinopathy is a chronic complication of diabetes, which is caused by damage to the vessels of the retina as a result of a prolonged increase in blood glucose.
____________
2. Type 1 diabetes mellitus
In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, this complication can appear only as a result of poor control of glucose levels for a long period of time; in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, manifestations of retinopathy can already be observed at the stage of diagnosis.
____________
3. diabetes need to be examined
All people with diabetes need to be examined by an ophthalmologist at least 1 time per year.
check here first before it will go worse
____________
4. The most initial stage of retinopathy
The most initial stage of retinopathy is non-proliferative. At this stage, there is an expansion of small vessels and the formation of aneurysms (protrusion of the walls of blood vessels).
____________
5. Macular edema
Macular edema is a lesion of the central part of the retina, as a result of the exit of fluid from damaged vessels. An eye with macular edema sees a cloudy, blurry picture. To identify macular edema, it is necessary to conduct a self-examination using the Amsler mesh, which can be obtained from an ophthalmologist.
____________
6. The proliferative stage of retinopathy
The proliferative stage of retinopathy is characterized by the appearance of newly formed vessels with a very fragile wall, damage to which leads to hemorrhage.
____________
7. The development of nephropathy
As with retinopathy, the development of nephropathy is based on vascular damage. Therefore, if signs of retinopathy are detected, it is also necessary to evaluate renal function.
____________
8. Vitreous hemorrhage
A formidable complication of proliferative retinopathy is vitreous hemorrhage. The first signs of hemorrhage are the appearance of blurred vision, floating blackouts in front of the eyes.
____________
9. Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is another dangerous complication of retinopathy. Most often, it is manifested by the appearance of shadows, fogging in the field of view.
____________
10. Laser coagulation
Laser coagulation is one of the most important treatments for retinopathy. With the help of a laser, “newly-formed vessels” “cauterize”, and “retention” of the retina also occurs.
____________
11. Another method of treating retinopathy
Another method of treating retinopathy is the intraocular administration of drugs that block the formation of new, pathological (“bad”) vessels.
____________
12. Maintain satisfactory control of diabetes
However, the most important treatment for retinopathy is to maintain satisfactory control of diabetes.
____________
13. Your target glucose values
In the presence of proliferative retinopathy, too rapid a decrease in blood glucose can worsen the condition of the fundus. Talk with your healthcare provider about your target glucose values.
____________
14. The presence of retinopathy
The presence of retinopathy is not a contraindication for the birth of children, however, if retinopathy is in the proliferation stage, it is necessary to treat it before conception.
____________
15. It is recommended to avoid lifting heavy objects
Also, in the presence of proliferative retinopathy, it is recommended to avoid lifting heavy objects, such as weightlifting and prolonged stay upside down.